For any integration developer building software for eCommerce, authentication in a REST API isn't just another technical checkbox—it's the digital passport control that guards every single piece of data flowing between systems. Think of it as the gatekeeper for an entire eCommerce ecosystem, verifying your app's identity before it can touch sensitive resources like customer orders, product catalogs, and inventory levels.
Why REST API Authentication Is Your First Line of Defense
Imagine your API is a secure warehouse full of valuable merchant data. Without a strong lock on the front door, anyone could wander in and walk out with sensitive information. That's what a missing or weak authentication method does. It opens the door to data breaches that can cost a company millions.
In a world powered by APIs, one tiny authentication flaw can expose merchant records, bring operations to a halt, and shatter trust for good. For an integration developer, getting authentication right is your most critical security responsibility. It's the absolute cornerstone of scalable and reliable eCommerce integrations, especially when you're working with unified platforms that connect dozens of shopping carts at once. Each connection point is a potential vulnerability, and solid identity verification ensures every request is legitimate.
The Challenge for Integration Developers
This is where things get messy for developers building for the eCommerce space. The landscape is incredibly fragmented. Integrating with major platforms like Shopify, Magento (Adobe Commerce), or WooCommerce means you're constantly bumping into different, and often inconsistent, security protocols.
One platform might use OAuth 2.0, another could rely on simple API keys, and a third might have its own proprietary method. This patchwork approach creates a ton of friction for your development workflow:
- Increased Complexity: You have to learn, implement, and then maintain completely different authentication logic for every single platform you connect with.
- Higher Maintenance Overhead: When a platform decides to update its security model—and they always do—you're on the hook to rewrite your integration to keep it from breaking.
- Greater Security Risks: Juggling a dozen different security methods is a recipe for mistakes. The more moving parts you have, the higher the chance of a misconfiguration that can be exploited.
How API2Cart Speeds Up Development
This is exactly where a unified API solution like API2Cart becomes a game-changer for an integration developer. Instead of building and maintaining dozens of separate, fragile authentication mechanisms, you only have to manage one.
Use Case: An inventory management system needs to connect to 15 different shopping carts. Without a unified API, a developer would spend weeks, if not months, implementing 15 unique authentication flows. With API2Cart, they implement one authentication method and can start syncing inventory data across all 15 platforms in a fraction of the time.
By standardizing the authentication process, API2Cart frees you up to focus on what actually matters: building great features for your customers instead of wrestling with security protocols. You can connect to a new shopping cart in minutes, not weeks, and do it with confidence, knowing the authentication is handled securely and consistently across every single integration.
Comparing Core Authentication Methods for Developers
For an integration developer, picking the right method for authentication in a REST API is like choosing the right key for a lock. You wouldn't use a simple padlock on a bank vault, and you definitely don't need a biometric scanner for a garden shed. Each method strikes a different balance between simplicity, security, and flexibility.
Getting this choice right is critical. The wrong approach can expose security holes or bog you down in needless complexity, stalling your project and putting data at risk. Let's walk through the most common methods from the perspective of a developer building integrations.
API Keys: The Secret Handshake
Think of an API Key as a simple, pre-arranged secret handshake. It's a long, unique string of characters you pass along with your request, usually in a header, just to say, "Hey, it's me."
This method is incredibly straightforward and perfect for server-to-server communication where there's no end-user clicking buttons. It’s a solid fit for internal services or for granting access to public, non-sensitive data. But its biggest weakness is its simplicity. If an API key ever gets exposed—say, it's accidentally committed to a public code repository—anyone can use it.
- Pros: Very easy to implement and use.
- Cons: Not secure if leaked; offers no granular user permissions.
- Best For: Internal services, server-to-server calls, and accessing public data where the risk of exposure is low.
Basic Authentication: The Straightforward Password
Basic Authentication is the digital equivalent of a simple username and password. The client just sends a Base64-encoded string of username:password in the Authorization header with every single request.
While that sounds easy, it's also its biggest flaw. Base64 is just an encoding format, not encryption. Anyone who intercepts the request can instantly decode the credentials. Because of this, Basic Auth is only considered remotely safe when used exclusively over an HTTPS connection, which encrypts the entire request pipeline.
- Pros: Simple to understand and universally supported.
- Cons: Insecure without HTTPS; credentials are sent with every request.
- Best For: Simple internal APIs where HTTPS is strictly enforced and you just need a quick, no-frills solution.
OAuth 2.0: The Valet Key
OAuth 2.0 is the industry standard for secure, delegated access. The best analogy is a valet key for your car. You don't hand the valet your master key that opens the trunk and glove box; you give them a special key that only lets them park the car.
In the same way, OAuth 2.0 lets an end-user grant your application specific, limited permissions to access their data on another service without ever sharing their actual username and password with you. It revolves around access tokens with defined "scopes" (permissions) and is the go-to for third-party integrations, like allowing your app to pull order data from a merchant's Shopify store on their behalf.
The complexity of implementing OAuth 2.0 across different eCommerce platforms is a massive headache for integration developers. Each platform has its own quirks, token refresh logic, and error handling, creating a huge maintenance burden.
This is exactly where a unified solution like API2Cart comes in. API2Cart handles all the platform-specific OAuth 2.0 flows for you. As a developer, you connect once using a single, consistent authentication method, and API2Cart manages the messy, behind-the-scenes token negotiations with platforms like Shopify or Magento. It completely slashes integration time and removes a major security obstacle.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): The Digital Passport
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are like a self-contained digital passport. After a user authenticates, the server creates a signed JWT that contains claims about the user—their identity, permissions, and so on—and sends it back to the client. The client then includes this JWT in the header of every subsequent request.
The beauty of this is that the server can verify the token's signature to confirm its authenticity without having to look up session information in a database. This "stateless" nature makes JWTs incredibly efficient and scalable, especially for microservices architectures. You can dig deeper into the differences by exploring this comparison of API authentication methods.
- Pros: Stateless, secure (if signed correctly), and highly scalable.
- Cons: Tokens can get large; cannot be easily revoked before they expire.
- Best For: Securing stateless APIs, single-page applications (SPAs), and mobile apps where managing server-side sessions is a pain.
To help you quickly compare these options, here's a simple breakdown of how they stack up against each other for common integration scenarios.
REST API Authentication Methods At a Glance
| Method | Primary Use Case | Security Level | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Keys | Server-to-server, public data | Low | Very Low |
| Basic Auth | Simple internal APIs (with HTTPS) | Low | Very Low |
| OAuth 2.0 | Third-party user-delegated access | High | High |
| JWT | Stateless APIs, SPAs, mobile apps | High | Medium |
Ultimately, the right choice depends entirely on your specific use case—who is accessing the data, how sensitive is it, and how much complexity can your team handle? Choosing wisely upfront saves a world of trouble down the line.
Securing High-Volume eCommerce Integrations
When you're an integration developer building for high-volume eCommerce, the rules of the game change. The standard methods of authentication in a REST API are a good starting point, but protecting data at scale demands more sophisticated security patterns. The potential fallout from a security slip-up grows exponentially when you're handling thousands of API calls an hour across dozens of merchant stores.
Simply authenticating a request isn't enough. You have to manage the entire lifecycle of your credentials to keep risk to a minimum. This means putting a laser focus on robust token management—generating, refreshing, and securely revoking access when it's no longer needed. The goal is to shrink the window of opportunity for an attacker if a credential ever gets compromised.
The Refresh and Access Token Pattern
A crucial pattern for maintaining secure, long-term connections is the use of short-lived access tokens paired with long-lived refresh tokens. Think of the access token as a temporary keycard to a hotel room that expires in an hour. It gets you in the door right now but becomes useless quickly, which limits the damage if you lose it.
The refresh token, on the other hand, is like the front desk's permanent record of your stay. It’s a more secure, long-term credential that you don't flash around with every request. When your hourly keycard (the access token) expires, your application quietly shows the refresh token to the authentication server to get a new one. This all happens without bothering the user to log in again.
This two-token strategy gives you the best of both worlds:
- Enhanced Security: A leaked access token is only valuable for a very short time, which dramatically reduces its appeal to an attacker.
- Improved User Experience: The application can stay logged in for the long haul without constantly bugging the user for their password, creating a smooth, uninterrupted workflow.
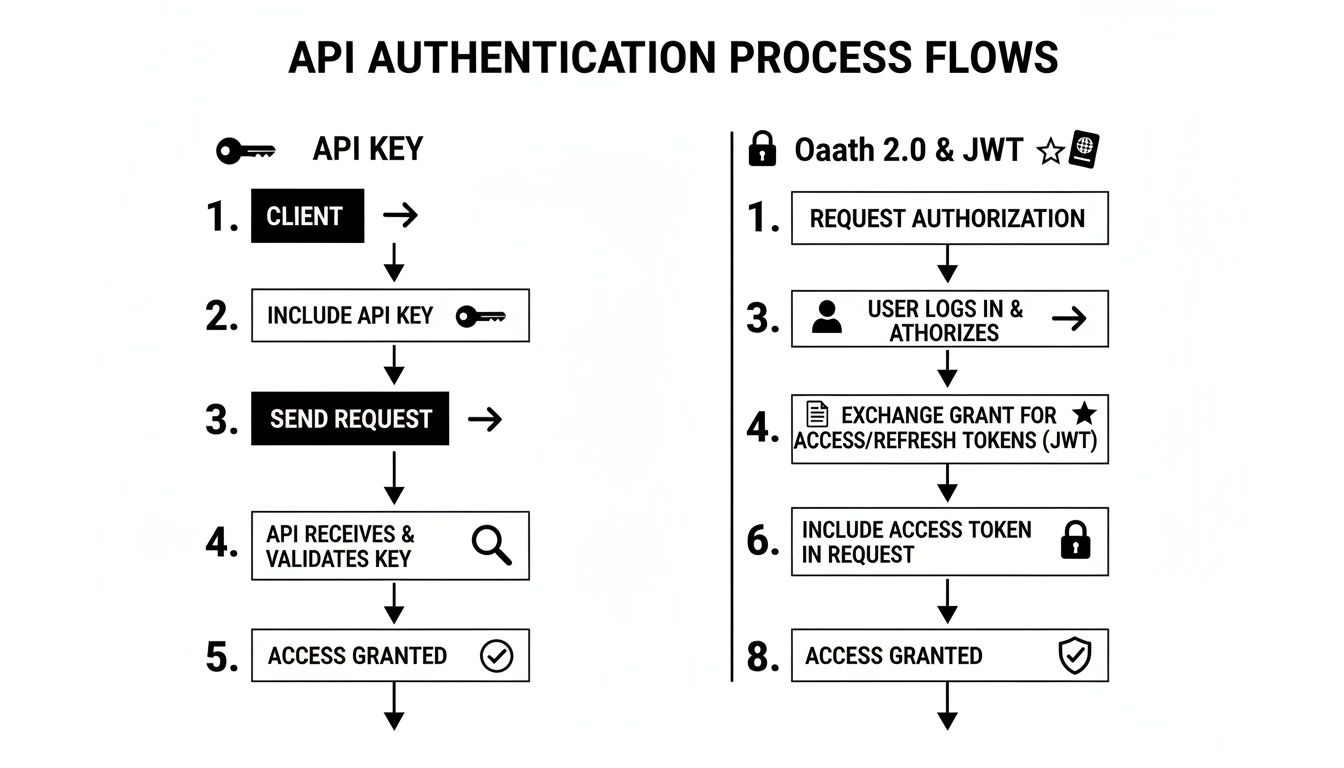
This flowchart shows the fundamental differences between a simple API Key workflow and the more complex, secure dance of methods like OAuth 2.0 and JWTs.
As you can see, OAuth 2.0 and JWTs introduce extra steps like user consent and token exchange. These steps are exactly what make the powerful access and refresh token pattern possible.
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege
Another concept you can't afford to ignore as a developer is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). This is just the technical term for the "principle of least privilege." Put simply, your application should only have permission to access the data and perform the actions it absolutely needs to do its job—and nothing more.
For instance, an order management app needs to read and write order data. It has no business modifying a store's theme settings or touching customer payment details. By defining strict roles and scopes, you create a firebreak. If your application is ever compromised, the breach is contained to only the data it was authorized to see, preventing a catastrophic, system-wide failure.
The fact that 95% of security incidents involve credential abuse in authenticated sessions is a wake-up call. It makes robust REST API authentication a matter of survival. This lines up with wider trends showing that 66% of disclosed web app infrastructure secrets were JWTs used for authentication, proving just how often token mishandling opens the door for breaches.
This really hammers home the point: it’s not just about authenticating users, but also about strictly controlling what they can do after they're in. For more context on securing financial data in high-volume eCommerce, the insights from payments experts can be incredibly valuable.
How API2Cart Simplifies Advanced Security
Let's be honest: implementing these advanced patterns is a heavy lift for any developer. Managing token lifecycles, refresh logic, and granular RBAC is complex enough for one platform. Now, imagine doing it for 60+ different eCommerce platforms. Each one has its own quirky API, its own way of handling token expiration, and its own unique permission models.
Use Case: A marketing automation platform needs to retrieve customer and order data, but should never access payment information. A developer would normally need to implement complex scope and permission logic for each shopping cart. With API2Cart, they can set these permissions once within a unified system, ensuring the principle of least privilege is enforced consistently everywhere without platform-specific code.
This standardization through API2Cart dramatically cuts down development time and eliminates a huge source of potential security flaws, letting you focus on building your application's logic with the confidence that the underlying authentication is handled securely and reliably across every single platform.
How a Unified API Solves the Authentication Puzzle
Imagine the chaos. As an integration developer, you're tasked with connecting your software to Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, and a dozen others. Each one greets you with a completely different security protocol. Shopify uses OAuth 2.0 with specific scopes, Magento has its own token logic, and some smaller platforms might still be using simple API keys. This is the authentication puzzle that drains engineering resources and stalls projects.
This fragmentation isn't just an inconvenience; it's a huge roadblock. Building and maintaining dozens of different security models means your team has to become experts in the unique quirks of every single platform. It’s a constant battle of digging through dense documentation, writing custom code for each integration, and troubleshooting platform-specific errors. The result? A multi-week integration project for each new platform—an unacceptable delay in today's competitive market.
Abstracting Away the Complexity
This is where a unified API like API2Cart completely changes the game for a developer. Instead of forcing you to solve the same authentication puzzle over and over, it abstracts the entire process away. You no longer need to write custom logic for each platform's unique flavor of OAuth or token negotiation.
You just interact with a single, consistent, and predictable authentication mechanism. You authenticate once with API2Cart using a straightforward API key, and that's it. Your part is done.
Behind the scenes, API2Cart acts as your expert security translator. It handles all the complex, platform-specific handshakes—the OAuth 2.0 flows, the token exchanges, and the credential management—for every single one of the 60+ supported shopping carts.
This shift is profound. What was once a daunting, time-sucking security challenge becomes a single, simple step. You can connect a new merchant's store and start syncing data almost immediately, letting you focus your engineering talent on building features, not security plumbing.
Speeding Up Development and Reducing Overhead
The benefits for an integration developer are immediate and massive. By standardizing the authentication process, a unified API eliminates the need to write and maintain brittle, platform-specific code. This dramatically cuts down your time-to-market.
Think about these practical use cases where API2Cart speeds things up for developers:
- Rapid Onboarding for New Merchants: When a new customer wants to connect their WooCommerce store, a developer doesn't need to spend days implementing the OAuth 2.0 flow. With API2Cart, you simply guide the merchant through a one-time authorization, and the connection is live in minutes.
- Zero-Maintenance Security Updates: When a major platform like Shopify updates its authentication protocol, your team doesn't have to scramble to patch your integration. API2Cart manages these changes on its end, ensuring your connection remains stable and secure with zero effort from you.
- Simplified Error Handling: Instead of deciphering cryptic, platform-specific authentication errors, you work with a standardized set of responses from one API. This makes debugging faster and more efficient, reducing downtime and frustration.
Freeing Resources for Core Business Logic
Ultimately, the biggest win is focus. Every hour your team spends wrestling with a different method of authentication in a REST API is an hour not spent improving your product. A unified API hands those hours right back to you.
By offloading the entire authentication puzzle, API2Cart allows your engineers to concentrate on the core business logic that actually delivers value to your customers. Whether you're building an order management system, an inventory synchronization tool, or a marketing automation platform, your team can build better software, faster. This pivot from managing security complexity to building product features is what gives you a critical competitive edge.
Verifying Webhooks for Real-Time Data Security
While traditional authentication in a REST API is all about securing requests your application makes to a server, there's another crucial data flow that integration developers often miss: webhooks.
Webhooks are basically reverse APIs. Instead of you calling the server for updates, the server calls you to deliver information in real time. Without a solid verification process, this opens up a massive security hole in your application.
Think of it like getting a critical package delivered. You wouldn't just accept a box from anyone who knocks on your door. You’d check the delivery person's ID to make sure they're legitimate. Webhook verification is that digital ID check for incoming data.
Why Unverified Webhooks Are a Major Risk
If your application blindly accepts any data sent to its webhook endpoint, an attacker can easily send fake payloads. This could be disastrous, especially in an eCommerce context.
Use Case: An order management system relies on webhooks to process new orders. A malicious actor could send a fraudulent "new order" payload, tricking your system into shipping products for free. Or they could send a fake "order canceled" event, causing lost revenue and seriously confused customers. This makes webhook security an absolute must-have for your integration strategy.
How to Secure Webhooks with HMAC Signatures
The industry-standard method for locking down webhooks is using a Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC). This process creates a verifiable signature to prove two things: the webhook came from the right place, and its content hasn't been messed with along the way.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works from a developer's point of view:
- Generate a Shared Secret: When you set up a webhook, your app and the eCommerce platform agree on a secret key that only the two of them know.
- The Platform Signs the Payload: Before sending you a notification, the platform combines the webhook payload with the shared secret using a hashing algorithm (like SHA-256). This creates a unique signature, which gets sent along in the request header.
- Your Application Verifies the Signature: When your application gets the webhook, it runs the exact same calculation. It takes the payload it received, combines it with its copy of the shared secret, and generates its own signature.
- Compare and Validate: Finally, your application compares the signature it just created with the one sent in the header. If they match, you can be 100% certain the webhook is authentic and untampered. If not, you throw the request out immediately.
This cryptographic handshake is all about data integrity. It’s the digital version of a wax seal on an old letter—if the seal is unbroken, you know the message is genuine and hasn't been read or changed. To see this in action, check out this detailed web hook example and its implementation.
Standardizing Webhook Verification with API2Cart
Here’s the rub for integration developers: every eCommerce platform does webhook verification a little differently. They might use different hashing algorithms, stick the signature in different headers, or handle edge cases in their own quirky ways. Trying to manage this across dozens of platforms is a massive headache.
This is where a service like API2Cart really shines. API2Cart standardizes the entire webhook process, security included. As a developer, you implement one verification logic for API2Cart's webhooks, and our platform handles the specific signature schemes for each of the 60+ supported shopping carts behind the scenes. This simplifies development, slashes security risks, and lets you build real-time features like order import automation with complete confidence.
Common Authentication Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best intentions, it's surprisingly easy to fall into common traps when implementing authentication in a REST API. These aren't just minor coding errors; they're security holes that can quickly lead to major data breaches. Knowing what these pitfalls look like is the first step to building integrations that are genuinely resilient and secure.
In the fast-paced world of digital integrations, broken authentication is a massive vulnerability. In fact, it accounts for nearly 30% of all surveyed API incidents, according to recent security analyses. Attackers are always looking for the low-hanging fruit—missing auth on sensitive endpoints, predictable API keys, or replay attacks that let them slip past your defenses.
Gartner drives this point home, noting that APIs are still the number one application attack vector. A staggering 95% of attacks happen after a session is authenticated, not from anonymous probes. You can discover more insights about these REST API security best practices on Levo.ai.
Forgetting Server-Side Validation
One of the most critical mistakes a developer can make is trusting a token just because it looks right. For example, a JWT can be decoded on the client side without any issue, but that tells you nothing about whether it's actually valid. You absolutely must verify the token's signature on the server using a securely stored secret key.
Without that server-side check, an attacker could forge a token, give themselves admin permissions, and walk right in. It’s a simple oversight that completely defeats the purpose of using tokens in the first place. If you're curious about the nuts and bolts, we have a deeper dive into the differences between OAuth vs JWT security models.
Ignoring Rate Limiting on Authentication Endpoints
Your authentication endpoints are a prime target for brute-force attacks. This is where attackers throw thousands of password guesses at your login routes every second, hoping one will stick. Without rate limiting, your API is a sitting duck.
Implementing rate limiting is non-negotiable for developers. It should lock out an IP address or user account after just a handful of failed attempts. This makes automated attacks impractical for the attacker and very, very noisy.
Overlooking the Complexity and How API2Cart Helps
Now, imagine trying to manage all these security details across dozens of different eCommerce platforms. It’s a massive undertaking for any developer. Each platform has its own unique authentication flow, its own token validation rules, and its own security quirks. It's easy for a developer to misconfigure one integration while getting another right, creating an inconsistent and dangerous security posture.
This is where a unified API like API2Cart brings tremendous value. Instead of forcing you to become a security expert on 60+ platforms, API2Cart handles the nitty-gritty of authentication, validation, and security best practices behind a single, consistent API. You get to connect to stores quickly and securely, confident that the common pitfalls have already been handled by a specialized team. It frees you up to focus on what you do best: building your application's features.
Common Questions About REST API Authentication
When you're deep in the trenches of building eCommerce integrations, a few common questions about authentication in a REST API always seem to pop up. Let's clear up some of the most frequent ones from a developer's standpoint.
What Is the Most Secure Method for REST API Authentication?
Hands down, OAuth 2.0 is the industry gold standard for both security and flexibility. It really shines in situations where a user needs to give your application limited access to their data without ever handing over their main username and password. The whole system is built around scopes, which gives you as a developer incredibly granular control over exactly what your app is allowed to do.
Can I Use Multiple Authentication Methods on One API?
Of course. In fact, it’s not just possible—it’s a smart and very common practice. You might see an API that uses straightforward API keys for trusted, internal server-to-server calls, but then requires the full OAuth 2.0 flow for any third-party, user-facing apps. This lets you match the right level of security to the right use case.
As APIs become more central to business, weak authentication remains a huge blind spot. It's a factor in nearly 30% of security incidents, and with over 80% of organizations struggling with API security, getting authentication right isn't just a "nice-to-have"—it's a must. You can dig deeper into these API security trends on Curity.io.
How Does Authentication Differ from Authorization?
Here’s a simple analogy for developers: think about getting into a secure office building.
Authentication is proving who you are. It's like showing your photo ID to the guard at the front desk. They verify your identity.
Authorization is what you're allowed to do once you're inside. It's the keycard the guard gives you, which only grants access to certain floors or rooms. One verifies identity, the other enforces permissions.
For developers juggling dozens of platform integrations, implementing and maintaining all these different authentication methods is a huge headache. This is where a unified API like API2Cart comes in. It abstracts away all that platform-specific complexity. You authenticate once to a single endpoint, and API2Cart handles the intricate logic for each platform behind the scenes, saving you massive amounts of development time and cutting down on security risks.
Stop wasting valuable engineering hours on building and maintaining dozens of separate, complex integrations. With API2Cart, you can connect to over 60 shopping carts and marketplaces through a single, unified API. Start your 14-day free trial today and see how quickly you can expand your market reach.