As an e-commerce service provider, you will often find success by focusing on the needs of your customers.
It doesn’t matter if you offer a chatbot tool, marketing automation system, CRM solution, or what have you. Other than helping them get more sales through the services you provide, they need you to be dependable when it comes to the security of their data.
Slip up once and the damage to your brand’s reputation might be irreversible, especially in the B2B sphere where cybersecurity breaches can easily cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
In this post, we’ll take a look at the most effective cybersecurity practices that can keep your e-commerce platform airtight.
Let’s get started.
1. Focus on payment security
It’s not hard to see why payment security is important to online retailers.
In addition to protecting their customers and their image from cyber threats, secure badges from payment gateways like PayPal can also build buyer confidence.

Naturally, e-commerce businesses know better to choose service providers that can guarantee secure payments. If you cater to local businesses, lean away from check-based payments and towards digital transactions supported by enterprise-grade encryption.
Storing your customers’ data must also be left off the table since its benefits are nowhere near enough to match the risks.
Online retailers also pay attention to the verification of service providers they purchase from. As such, consider an identity verification services like Jumio and Trulioo.
It also helps to ensure compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) to gain the trust of finicky B2B buyers.
2. Get a CDN
One of the biggest cybersecurity threats on the web right now is a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack.
As the name suggests, DDoS attacks deny legitimate users access to a web service or product by flooding a server with malicious traffic. These attacks require a network of infected systems — also known as botnets — to generate the traffic needed to exhaust a server’s bandwidth capacity.
Most website security solutions that feature a Web Application Firewall (WAF) also have integrated DDoS protection. Alternatively, service providers can subscribe to a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to mitigate the massive influx of traffic across multiple servers.
In simple terms, a CDN is a collection of proxy servers that share the workload of storing, managing, and transferring website data to nearby users. Aside from DDoS protection, CDN services also reduce latency for users around the globe, which improves their experience and make them more likely to convert.
3. Upgrade your hosting
Speaking of DDoS protection, premium website hosting providers like HostGator have a similar feature implemented for all hosting packages.
Of course, not all hosting companies offer the same benefits to their customers. That’s why you need to keep DDoS protection, vulnerability scanners, and other security features in mind when choosing a web host for your platform.
Another point to consider is the capability of a host to maximize uptime.
Although downtimes cannot be fully eliminated, you need to go with a hosting provider that won’t plague your site with frequent downtimes that affect profits, ruin the experience of your customers, and compromise your website’s search engine rankings.
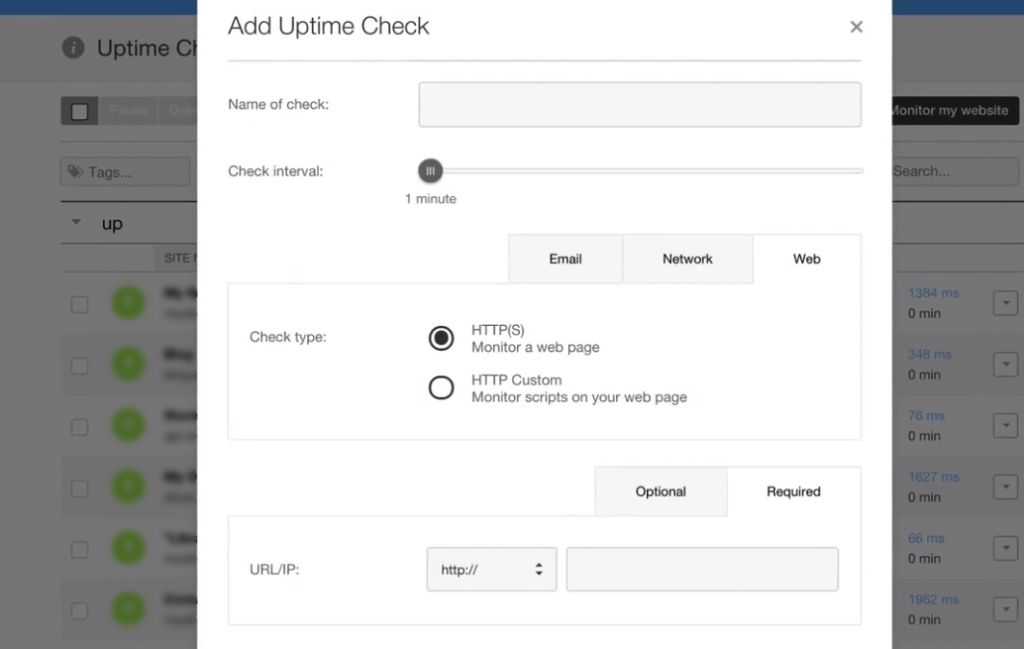
Using a tool like Pingdom Uptime Monitoring is a great way to put your hosting provider to the test and influence any decisions to upgrade down the line.
4. Focus on employee training
Whether you like it or not, human error is still the number one contributor to cybersecurity breaches in the business world.
Even if you have the most powerful security software in the market, it only takes one uninformed employee who has no clue about cybersecurity to compromise your systems.
Poor password hygiene, for example, grant an attacker uninterrupted access to your backend. And while you may think everyone has outgrown the use of weak passwords by now, statistics show that there are still people who use passwords like “12345,” “letmein,” and “iloveyou.”
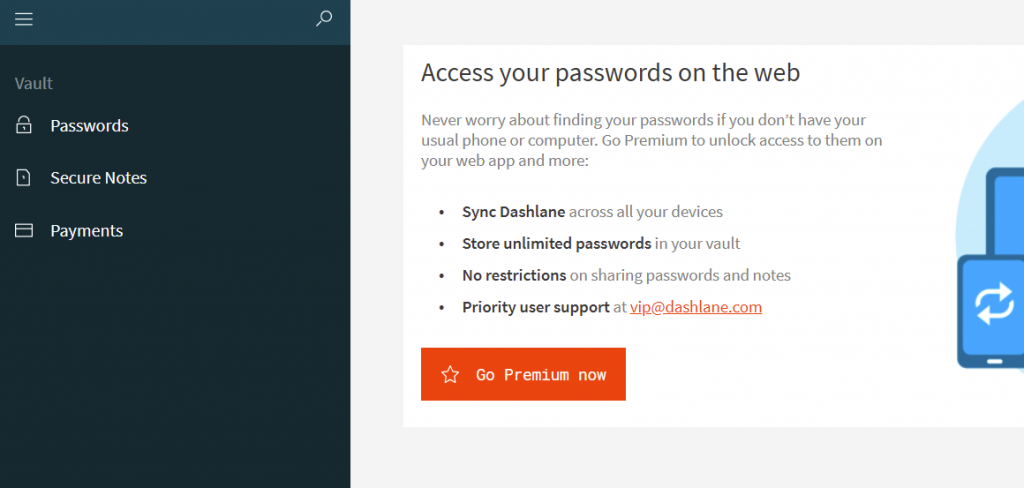
A quick solution is to encourage employees to use password managers like Dashlane, which enables the use of strong, unique passwords for all accounts without having to memorize each of them. It also supports two-factor authentication — a feature that restricts access to a user’s data unless they can fulfil another verification method, like a one-time password or biometric information.
To lessen the likelihood of breaches due to human error, make employee cybersecurity training one of your priorities.
Aside from password security, below are some of the subjects you need to cover when training your employees:
- Phishing
Phishing scams occur when a hacker uses a replica of an email from a well-known service provider to fool users into providing their credentials. Employees need to be aware of the fundamental practices that avoid phishing scams, like an analyzing the email signature, calling the company’s support hotline for verification, and ignoring attachments or links that are suspicious in nature.
- Malware Infections
There are many ways for malware to infect your organization’s network, such as through removable storage devices, software bundle downloads, and peer-to-peer file sharing. Blocking your network’s access to certain, unsafe domains is a step in the right direction along with effective Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies.
- Digital Eavesdropping
In the online world, eavesdropping pertains to the act of getting unauthorized access to a communication channel — from instant messaging apps to email clients — without the knowledge of the actual participants. This can be effectively prevented by avoiding public Wi-Fi networks or using encrypted communication services or tools.
5. Keep your software up-to-date
Be it a Content Management System (CMS), antivirus program, or Operating Systems (OS), software vendors constantly roll out updates to protect against the latest vulnerabilities.
In most cases, updates also come with potential bug fixes, performance improvements, and additional features.
Make sure you are always protected by enabling an automatic update feature when available. If not, see to it that your team manually checks for software updates at least once a month.
For most cloud applications, updates are normally downloaded and installed on the server side. This means you don’t have to worry about long download times and the loss of productivity due to hardware resources being utilized in the background.
As a precaution, create regular backups before you install software updates, especially if the changes will be applied locally in your organization’s devices. Other than cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox, you can create local backup with tools like Acronis and Paragon Backup & Recovery.
6. Invest in threat intelligence
If there’s one thing most cybersecurity applications can’t stop, it’s a zero-day attack — a software vulnerability exploited by hackers before the program vendor or cybersecurity companies can design a countermeasure and send out updates.
While a zero-day attack can be inevitable at times, you can leverage the power of artificial intelligence to drastically reduce the possibility of being affected.
Cyber threat intelligence services like F-Secure and Darktrace utilize machine learning to predict, detect, and prevent cyber-attacks — including zero-day exploits — from ever touching your platform.
The good news is, threat intelligence services are often bundled with essential cybersecurity tools, like antivirus, email security, and cloud protection. This makes them a cost-effective, all-in-one solution for enterprises that handle the data of thousands of customers.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity should be just as important to you as it is to online retailers and consumers.
Ultimately, it’s an initiative to create a safer and more productive internet for end users. It also guarantees the growth, sustainability, and success of your online brand.
What cybersecurity advice can you give e-commerce service providers and software developers? Feel free to leave a comment below!
In case you are looking for ways to effectively improve your product, try API2Cart. It provides a unified API to integrate with 60+ shopping carts and marketplaces including Magento, Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Amazon, eBay and others. Just schedule a call with our representative or try how API2Cart would work for your business.